
The optic tract gives off fibers that synapse and excite the mesencephalic olivary pretectal nucleus (OPN), which is excited by light from the retina but is also modulated by output from the cerebral cortex. The nasal retinal fibers of each eye contribute to the optic nerve and cross at the optic chiasm joining temporal retinal fibers from the other eye where they continue as the optic tract to the visual cortex of the occipital lobe at the back of the brain. These impulses are integrated by six types of neuronal cells in a layered functional unit of photoreceptors and glial cells that form the optic nerve.

When light enters the eye, it is immediately converted to electrical impulses by specialized retinal rod and cone cells in the neuroretina.
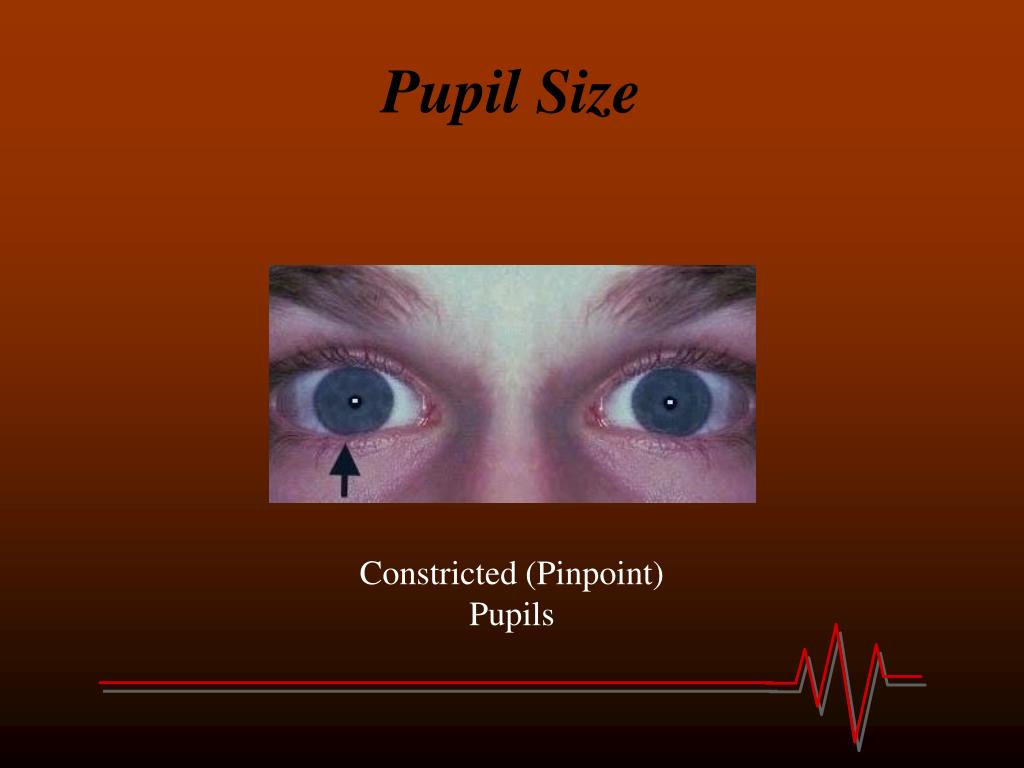
There is, therefore, a need to understand the neurophysiology associated with brain function that might modulate the PLR. The PLR represents a complexity of integration at many brain, brainstem, and spinal cord levels such that it should not be considered as a simple response to a light source stimulation. For instance, heart rate variability (HRV) is significantly correlated with PLR variables for evaluating the activity of the autonomic nervous system with the most robust measures of parasympathetic activity. PLR function is also correlated with other tests of autonomic function. This is due to central processing as a constant amount of light stimulation at a maintained luminance results in a different PLR response for males and females. Interestingly, the iris muscle is modulated by light stimulation activation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system resulting in higher parasympathetic and lower sympathetic activity in females compared to males, similar to the cardiovascular system. There are gender differences in autonomic function that are important clinically. Interestingly, constriction and dilation of the pupil may be more sensitive than other measures of autonomic function, with constriction dominated by the parasympathetic pathway and pupillary dilation dominated by the sympathetic system.

The PLR has been widely used to evaluate the activity of the autonomic nervous system. The attentional state of an individual, along with the size, luminance, and eccentricity of a stimulus, contributes to what was previously considered a simple reflex. It is essential to understand that the PLR is not a linear reaction of the pupil to light because pupil size is dramatically confounded by modest changes in attention, accommodation, and environmental ambient light. The PLR has probably been observed since the beginning of time and has become a standard examination tool used by all health care professionals after it was first described by Rhazes of Baghdad in the ninth century. The PLR, while considered an example of a basic neurological reflex, is not a simple reflex as its function is modulated by cognitive brain function and interaction with the superior colliculus (SC), pretectal olivary nucleus (PON), and locus coeruleus that regulate the PLR. This process is known as the pupillary light reflex (PLR). The size of our pupils changes continuously in response to variations in ambient light levels to regulate the amount of light entering our eyes. A concussive injury to the brain is associated with changes in the PLR that persist over the life span, representing biomarkers that might be used in clinical diagnosis, treatment, and decision making. The differences in PLR metrics are modulated not only by concussion history but also by gender and whether or not the person has symptoms associated with a head injury. There were also significant differences in PLR metrics over the life span and between genders and those subjects with and without symptoms. The PLR variables of latency, maximum pupil diameter (MaxPD), minimum pupil diameter (MinPD), maximum constriction velocity (MCV), and the 75% recovery time (75% PRT) were associated with significant differences between subjects who had suffered a concussion and those that had not. We performed a retrospective clinical review of the PLR of our patients using the BrightLamp Reflex iPhone app.
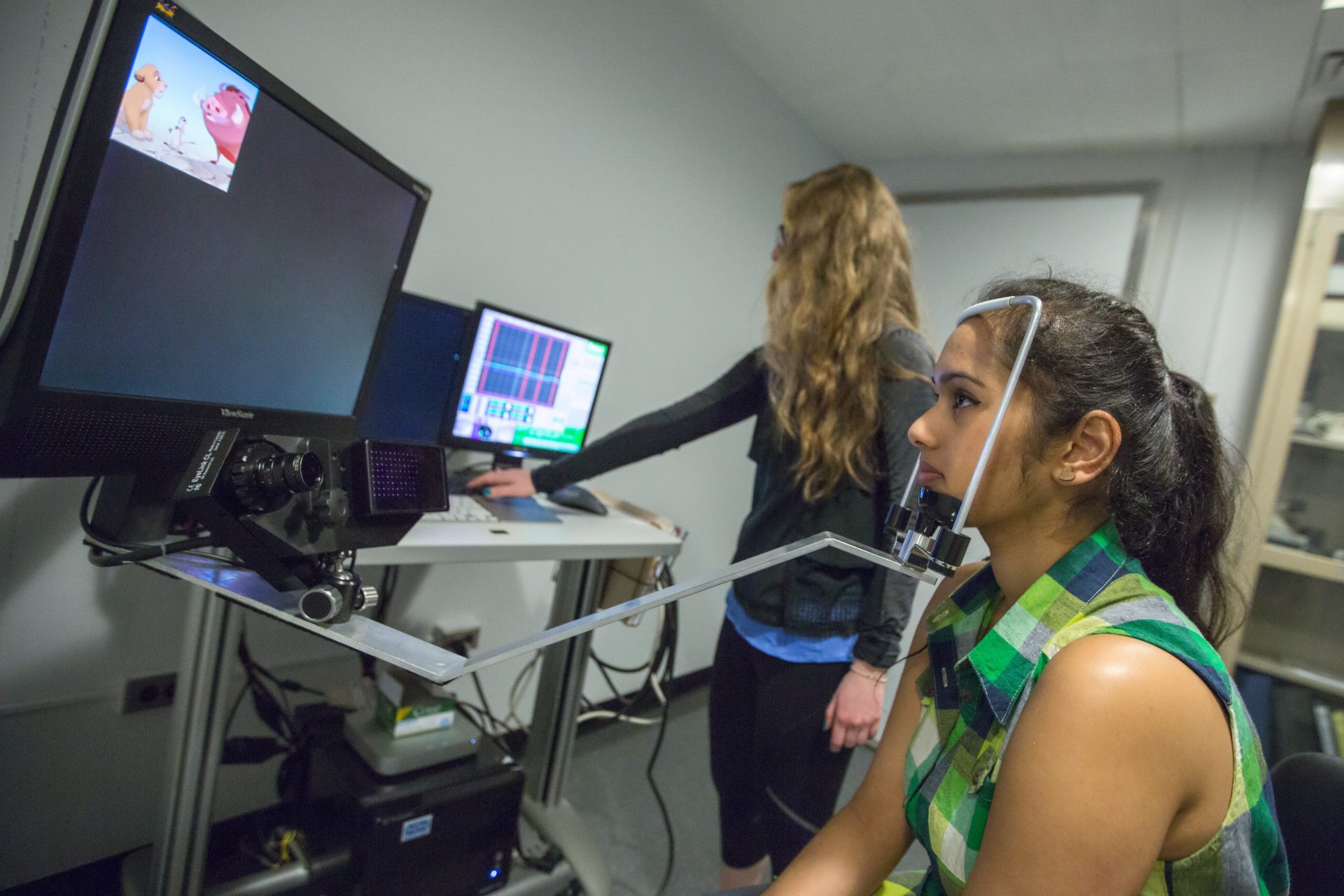
The PLR is not a simple reflex as its function is modulated by cognitive brain function and any long-term changes in brain function secondary to injury should cause a change in the parameters of the PLR. The size of our pupils changes continuously in response to variations in ambient light levels, a process known as the pupillary light reflex (PLR).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
